What is physical health?
Physical health can be defined as the normal functioning of the body. Representing one dimension of total well-being, it’s about how your body grows, feels and moves, how you care for it, and what you put into it.
Pillars of Physical Health
Maintaining good physical health decreases your risk of developing conditions such as heart disease, stroke and some cancers. Being physically healthy also helps you to manage life’s challenges by protecting you against fatigue, injury and illness.
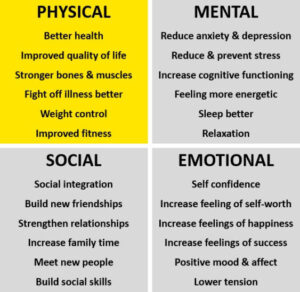
Physical health is closely linked to mental health and an integral part of leading a healthy lifestyle and enjoying life. This is often taken for granted and it isn’t until we are sick, ill or injured that we put the time and energy in to looking after our physical health. It is important to regularly monitor your overall physical health and getting a check-up if you (or someone you know) are concerned.
The four pillars of health are Sleep (and recovery), Nutrition, Physical Activity and Connection. The NZDF Health Hub provides everything you need to know about strengthening each of these pillars.
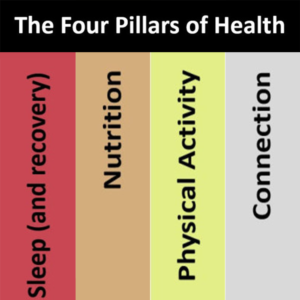
Sleep (and recovery)
Sleep is one of the most under-rated tools to enhance health and performance. Getting adequate sleep helps to prevent excess weight gain, heart disease and increased illness and disease.
Rest and recovery after stressful activity, both mentally and physically, is also important as it enables the body to repair itself and be fit and ready for another day.
More information can be found in the Sleeping well section.
Nutrition
Adequate and appropriate nutrition helps support performance, recovery, mental clarity, and overall mood.
Like a vehicle, the body performs best with the right fuel. If you put regular gasoline in a Formula 1 car, it will struggle to compete with the rest of the field and will likely end up making an early pitstop.
Good nutrition provides the body with the nutrients and fuel it needs to perform and recover. It also reduces stress and inflammation in the body, which is associated with injury, illness and mental health issues.
For detailed advice, see the Nutrition and supplements section. And check out this video explaining the surprisingly dramatic role of nutrition in mental health.
Physical Activity
The body is designed to move. Lack of exercise decreases range of motion within the body’s joints causing pain and dysfunction. It also contributes to a decline in physical, mental and physiological health. Sedentary behaviours can lead to a variety of health consequences including weight gain, type two diabetes, cardiovascular disease and mood disorders.
On the flip side, too much exercise and stress can have an adverse effect, making the body susceptible to burnout and a compromised immune system. The body functions best with moderate amounts of work, stress and activity, coupled with rest to allow the body to repair and build stronger.
Connection
Mental and physical health is fundamentally linked. There are multiple associations between mental health and chronic physical conditions that significantly impact people’s quality of life, demands on health care and other publicly funded services, and generate consequences to society. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines: health as a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity. The WHO states that “there is no health without mental health.”1
Nowhere is the relationship between mental and physical health more evident than in the area of chronic conditions. The associations between mental and physical health are:
- Poor mental health is a risk factor for chronic physical conditions.
- People with serious mental health conditions are at high risk of experiencing chronic physical conditions.
- People with chronic physical conditions are at risk of developing poor mental health.
What is mental health?
Mental health includes our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act. It also helps determine how we handle stress, relate to others, and make healthy choices.1 Mental health is important at every stage of life, from childhood and adolescence through adulthood.
Why is mental health important for overall health?
Mental and physical health are equally important components of overall health. For example, depression increases the risk for many types of physical health problems, particularly long-lasting conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. Similarly, the presence of chronic conditions can increase the risk for mental illness.
How does my mental health affect my physical health?
Research shows that people with a mental health problem are more likely to have a preventable physical health condition such as heart disease.
This can be for a variety of reasons, including:
- genetics – the genes that make it more likely that you will develop a mental health problem may also play a part in physical health problems
- low motivation – some mental health problems or medications can affect your energy or motivation to take care of yourself
- difficulty with concentration and planning – you may find it hard to arrange or attend medical appointments if your mental health problem affects your concentration
- lack of support to change unhealthy behaviour – healthcare professionals may assume you’re not capable of making changes, so won’t offer any support to cut down on drinking or give up smoking, for example
- being less likely to receive medical help – healthcare professionals may assume your physical symptoms are part of your mental illness and not investigate them further. People with a mental illness are less likely to receive routine checks (like blood pressure, weight and cholesterol) that might detect symptoms of physical health conditions earlier.
As well as this, mental health problems can come with physical symptoms. Our bodies and minds are not separate, so it’s not surprising that mental ill health can affect your body. Depression can come with headaches, fatigue and digestive problems, and anxiety can create an upset stomach, for example. Other symptoms can include insomnia, restlessness and difficulty concentrating.
What can I do to help myself?
Having a mental health problem doesn’t mean it’s inevitable that you will develop a physical health problem. There are things you can do to give yourself the best chance of staying physically well.
Exercise
Physical activity is a great way to keep you physically healthy as well as improving your mental wellbeing. Research shows that doing exercise releases feel-good chemicals called endorphins in the brain. Even a short burst of 10 minutes brisk walking can improve your mental alertness, energy and mood.
Whether you’re tending your garden or running a marathon, exercise can significantly improve your quality of life. Finding an activity you enjoy can make you feel less stressed, more focused, and give you a sense of purpose. For more tips on ways to get started, read our guide on how to look after your mental health using exercise.
Eat well
Eating well can improve your wellbeing and your mood. A balanced diet is one that includes healthy amounts of proteins, essential fats, complex carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals and water. The food we eat can influence the development, management and prevention of numerous mental health conditions including depression and dementia.
Stop smoking
Smoking has a negative impact on both mental and physical health. Many people with mental health problems believe that smoking relieves their symptoms, but these effects are only short-term. It’s never too late to quit, and there is now a lot of support available to help you give up.